پایگاه خبری تحلیلی 8دی نیوز
https://www.8deynews.com
میانمار کجاست؟ / Where is Myanmar?
Myanmar is a country in Southeast Asia. Myanmar shares the northeast with China, the east with Laos, the south-east with Thailand, the west with Bangladesh and the northwest with India.
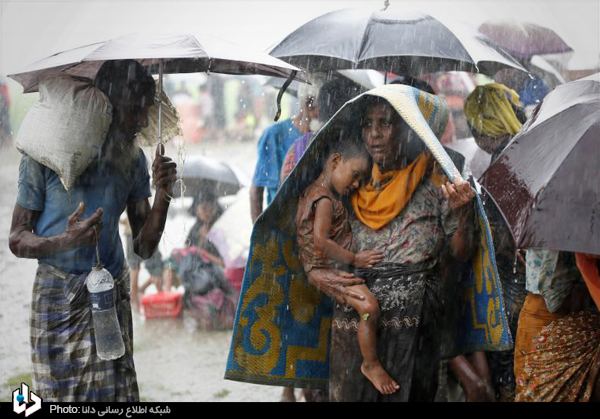

به گزارش ۸دی، میانمار کشوری است در آسیای جنوب شرقی. میانمار از شمال شرقی با چین، از شرق با لائوس، از جنوب شرقی با تایلند، از غرب با بنگلادش و از شمال غربی با هند مرز مشترک دارد و از جنوب غربی با خلیج بنگال و از جنوب با دریای آندامان محصور است. میانمار با مساحت ۶۷۸۵۰۰ کیلومتر مربع دومین کشور بزرگ آسیای جنوب شرقی است. این کشور ۱۹۰۰ کیلومتر مرز آبی دارد. در سال ۱۸۲۴ برمه Burma توسط بریتانیا اشغال و ضمیمه حکومت هند، مستعمره بریتانیا شد. در سال ۱۹۳۷ بریتانیا برمه را به همراه منطقه «آراکان» (Arakan) که اکنون به آن راخین Rakhine نیز میگویند، مستعمرهای جدا از حکومت هند خواند و آن را برمه بریتانیا نام نهاد. تا اینکه در سال ۱۹۴۸ بریتانیا اجازه داد تا برمه استقلال یابد و از آن زمان به «میانمار» تغییر نام یافت. میانمار طبق آخرین آمار بدست آمده از جمعیتی بالغ بر ۵۵ میلیون نفر برخوردار است. ۷۰درصد میانمار بودایى هستند. در سال ۱۹۸۲ قانون حقوق شهروندی به تصویب رسید که به واسطه این قانون از میان ۱۴۴ اقلیت موجود در میانمار ۱۳۵ اقلیت حق شهروندی دریافت کردند و ۹ دسته از اقوام اقلیت از حق شهروندی محروم شدند که بزرگترین این اقلیتها، قوم روهینگیا Rohingya است. روهینگیا ۴% جمعیت میانمار را تشکیل میدهند و بیشتر در ایالت راخین در سواحل غربی میانمار ساکن هستند. آمار رسمی جمعیت روهینگیا ۶ میلیون نفر است اما طبق آمار غیر رسمی جمعیت این قوم که صد در صد آنها مسلمان هستند به ۸ میلیون نفر میرسد.
Myanmar (Burmese pronunciation: [mjəmà]),[nb 1][6] officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known as Burma and Myanmar (Burma), is a sovereign state located in the Southeast Asian region. Myanmar is bordered by India and Bangladesh to its west, Thailand and Laos to its east and China to its north and northeast. To its south, about one third of Myanmar’s total perimeter of 5,876 km (3,651 miles) forms an uninterrupted coastline of 1,930 km (1,200 mi) along the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The country’s 2014 census counted the population to be 51 million people.[7] Myanmar is 676,578 square kilometres (261,227 sq mi) in size. Its capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city and former capital is Yangon (Rangoon).[1] Myanmar has been a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) since 1997.
Early civilisations in Myanmar included the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu city-states in Upper Burma and the Mon kingdoms in Lower Burma.[8] In the 9th century, the Bamar people entered the upper Irrawaddy valley and, following the establishment of the Pagan Kingdom in the 1050s, the Burmese language, culture and Theravada Buddhism slowly became dominant in the country. The Pagan Kingdom fell due to the Mongol invasions and several warring states emerged. In the 16th century, reunified by the Taungoo Dynasty, the country was for a brief period the largest empire in the history of Mainland Southeast Asia.[9] The early 19th century Konbaung Dynasty ruled over an area that included modern Myanmar and briefly controlled Manipur and Assam as well. The British took over the administration of Myanmar after three Anglo-Burmese Wars in the 19th century and the country became a British colony. Myanmar was granted independence in 1948, initially as a democratic nation and then, following a coup d’état in 1962, a military dictatorship.
۷۰% of Myanmar are Buddhists. In 1982, the Law on Citizenship was enacted that, according to this law, 144 minorities in Myanmar received 135 citizenship rights and nine groups of minorities were deprived of citizenship rights, the largest of these minorities being Rohingya’s people. Rohingya is home to 4% of Myanmar’s population and mostly inhabits the Rachin state on the west coast of Myanmar. The official figures for the Rohingya population are 6 million, but according to the unofficial statistics of the population, 100 percent of whom are Muslims, reaches 8 million.
ورود اسلام به میانمار
تاریخ گسترش اسلام در میانمار به قرن اول هجرى برمىگردد. بعد از ظهور اسلام و گرایش اعراب و ایرانیان به اسلام، دریانوردان عرب و ایرانى مسافرتهاى دریایى خود را انجام مىدادند و در مسیر خود همچنین دستبه تبلیغ و دعوت مردم به اسلام مىزدند. بعدها بازرگانان مسلمان از مسیرهاى زمینى که از منطقه غربى میانمار و ایالت آراکان این کشور مىگذشت به مناطق غربى چین سفرمىکردند. بسیارى از این افراد در منطقه حاصلخیز و مستعد ساحلى آراکان، اقامت کردند و اولین مناطق مسلمان نشین را ایجاد کردند. تاجران چینى در نوشتههاى خود از مناطق ایرانىنشین در مرزهاى بین میانمار و یونن (ایالتى در جنوب غربى چین) در قرنسوم میلادى یاد کردهاند. امروز در حدود ۸ میلیون در میانمار هستند و یک زبان محلی به نام روهینگیا دارند که در واقع مسلمانان میانمار را امروز به همین نام میشناسند و این زبان هم ترکیبی از عربی، فارسی و ترکی است که نشان دهندۀ این است که اسلام از منطقۀ آسیای غربی به آن منطقه رفته است.
….
The entrance of Islam to Myanmar
The history of the spread of Islam in Myanmar dates back to the first century. After the advent of Islam and the Arab-Iranian orientation toward Islam, Arab and Iranian sailors carried out their maritime trips and, on their own, also promoted and invited people to Islam. Later, Muslim merchants traveled to western areas of China on land traversed from the western part of Myanmar and the state of Arak. Many of these people settled in the fertile and susceptible area of the Arak Island, creating the first Muslim regions. The Chinese businessmen have mentioned in the writings of Iranian regions on the borders between Myanmar and Yunnan (the state in southwestern China) in the third century. Today, there are about 8 million people in Myanmar and have a local language called Rohingya, which in fact names Myanmar’s Muslims today with the same name, and this language is a combination of Arabic, Persian and Turkish, which indicates that Islam is from the West Asian region Has gone to that area.








نظرات